5 Feature set and Requirements from Infrastructure ¶
Table of Contents ¶
-
5.2 Cloud Infrastructure Software Profiles features and requirements.
-
5.4 Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profiles features and requirements.
A profile RM Section 2.4 specifies the configuration of a cloud infrastructure node (host or server); profile extensions may specify additional configuration. Workloads utilise profiles to describe the configuration of nodes on which they can be hosted to execute on. Workload Flavours provide a mechanism to specify the VM or Pod sizing information to host the workload. Depending on the requirements of the workloads, a VM or a Pod will be deployed as per the specified Flavour information on a node configured as per the specified Profile. Not only do the nodes (the hardware) have to be configured but some of the capabilities also need to be configured in the software layers (such as Operating System and Virtualisation Software). Thus, a Profile can be defined in terms of configuration needed in the software layers, the Cloud Infrastructure Software Profile, and the hardware, the Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profile.
5.1 Cloud Infrastructure Software profile description ¶
Cloud Infrastructure Software layer is composed of 2 layers, Figure 5-1 :
-
The virtualisation Infrastructure layer, which is based on hypervisor virtualisation technology or container-based virtualisation technology. Container virtualisation can be nested in hypervisor-based virtualisation
-
The host OS layer
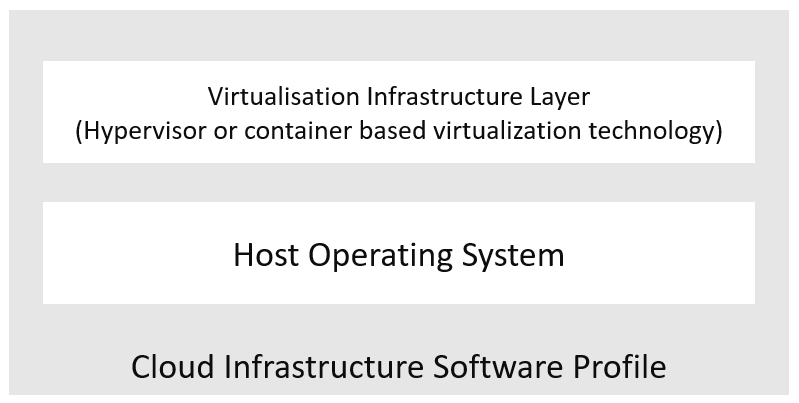
Figure 5-1: Cloud Infrastructure software layers
|
Ref |
Cloud In frastructure Software |
Type |
Defi nition/Notes |
Capabilities Reference 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.sw.001 |
Host Operating System |
Values such as Ubuntu20.04, Windows 10 Release #, etc. |
` e.cap.021` |
|
|
infra.sw.001 |
Vi rtualisation In frastructure Layer |
Values such as KVM, Hyper-V, Kubernetes, etc. |
` e.cap.022` |
1 Reference to the capabilities defined in Chapter 4 .
For a host (compute node or physical server), the virtualisation layer is an abstraction layer between hardware components (compute, storage, and network resources) and virtual resources allocated to a VM or a Pod. Figure 5-2 represents the virtual resources (virtual compute, virtual network, and virtual storage) allocated to a VM or a Pod and managed by the Cloud Infrastructure Manager.
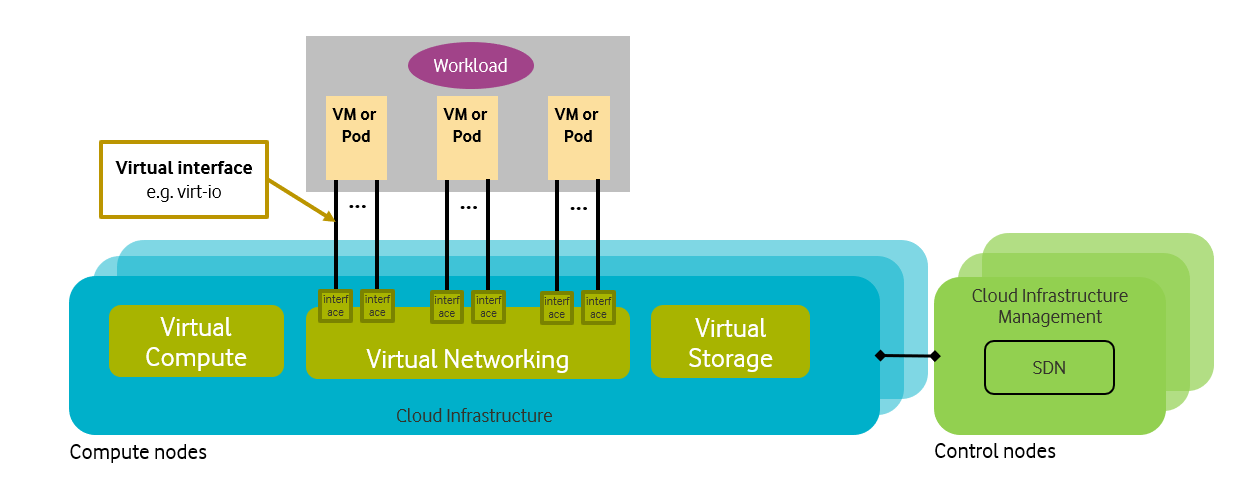
Figure 5-2: Cloud Infrastructure Virtual resources
A Cloud Infrastructure Software Profile is a set of features, capabilities, and metrics offered by a Cloud Infrastructure software layer and configured in the software layers (the Operating System (OS) and the virtualisation software (such as hypervisor)). Figure 5-3 depicts a high level view of the Basic and High Performance Cloud Infrastructure Profiles.
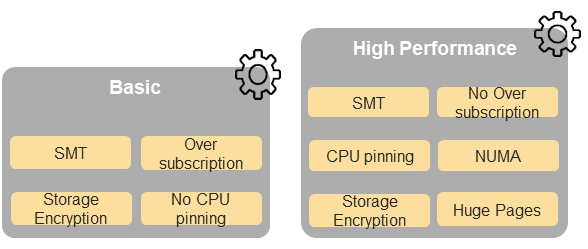
Figure 5-3: Cloud Infrastructure Software Profiles
The following sections detail the Cloud Infrastructure Software Profile capabilities per type of virtual resource.
5.1.1 Virtual Compute ¶
Table 5-1 and Table 5-2 depict the features related to virtual compute.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
Capabilities Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra .com.cfg.001 |
CPU allocation ratio |
Value |
Number of virtual cores per physical core. |
` i.cap.016` |
|
infra .com.cfg.002 |
NUMA alignment |
Yes/No |
Support of NUMA at the Host OS and vi rtualisation layers, in addition to hardware. |
` e.cap.007` |
|
infra .com.cfg.003 |
CPU pinning |
Yes/No |
Binds a vCPU to a physical core or SMT thread. Configured in OS and vi rtualisation layers. |
` e.cap.006` |
|
infra .com.cfg.004 |
Huge Pages |
Yes/No |
Ability to manage huge pages of memory. Configured in OS and vi rtualisation layers. |
` i.cap.018` |
|
infra .com.cfg.005 |
Simultaneous Mu ltithreading (SMT) |
Yes/No |
Allows multiple execution threads to be executed on a single physical CPU core. Configured in OS, in addition to the hardware. |
` e.cap.018` |
Table 5-1: Virtual Compute features.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
Capabilities Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.001 |
IPSec Acceleration |
Yes/No |
IPSec Acceleration |
` e.cap.008` |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.002 |
Transcoding Acceleration |
Yes/No |
Transcoding Acceleration |
` e.cap.010` |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.003 |
Programmable Acceleration |
Yes/No |
Programmable Acceleration |
` e.cap.011` |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.004 |
GPU |
Yes/No |
Hardware coprocessor. |
` e.cap.014` |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.005 |
FPGA/other Acceleration H/W |
Yes/No |
Non-specific hardware. These Capabilities generally require hardwa re-dependent drivers be injected into workloads. |
` e.cap.016` |
Table 5-2: Virtual Compute Acceleration features.
5.1.2 Virtual Storage ¶
Table 5-3 and Table 5-4 depict the features related to virtual storage.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
i nfra.stg.cfg.001 |
Catalogue Storage Types |
Yes/No |
Support of Storage types described in the catalogue |
|
i nfra.stg.cfg.002 |
Storage Block |
Yes/No |
|
|
i nfra.stg.cfg.003 |
Storage with replication |
Yes/No |
|
|
i nfra.stg.cfg.004 |
Storage with encryption |
Yes/No |
Table 5-3: Virtual Storage features.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.stg.acc.cfg.001 |
Storage IOPS oriented |
Yes/No |
|
|
infra.stg.acc.cfg.002 |
Storage capacity oriented |
Yes/No |
Table 5-4: Virtual Storage Acceleration features.
5.1.3 Virtual Networking ¶
Table 5-5 and Table 5-6 depict the features related to virtual networking.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
inf ra.net.cfg.001 |
Connection Point interface |
IO virtualisation |
e.g. virtio1.1 |
|
inf ra.net.cfg.002 |
Overlay protocol |
Protocols |
The overlay network encapsulation protocol needs to enable ECMP in the underlay to take advantage of the scale-out features of the network fabric. |
|
inf ra.net.cfg.003 |
NAT |
Yes/No |
Support of Network Address Translation |
|
inf ra.net.cfg.004 |
Security Groups |
Yes/No |
Set of rules managing incoming and outgoing network traffic |
|
inf ra.net.cfg.005 |
Service Function Chaining |
Yes/No |
Support of Service Function Chaining (SFC) |
|
inf ra.net.cfg.006 |
Traffic patterns symmetry |
Yes/No |
Traffic patterns should be optimal, in terms of packet flow. North-south traffic shall not be concentrated in specific elements in the architecture, making those critical choke-points, unless strictly necessary (i.e. when NAT 1:many is required). |
Table 5-5: Virtual Networking features.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
C apabilities Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.net. acc.cfg.001 |
vSwitch o ptimisation |
Yes/No and SW O ptimisation |
e.g. DPDK. |
`` e.cap.019`` |
|
infra.net. acc.cfg.002 |
SmartNIC (for HW Offload) |
Yes/No |
HW Offload |
`` e.cap.015`` |
|
infra.net. acc.cfg.003 |
Crypto a cceleration |
Yes/No |
`` e.cap.009`` |
|
|
infra.net. acc.cfg.004 |
Crypto A cceleration Interface |
Yes/No |
Table 5-6: Virtual Networking Acceleration features.
5.1.4 Security ¶
See Chapter 7 Security.
5.1.5 Platform Services ¶
This section details the services that may be made available to workloads by the Cloud Infrastructure.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
i nfra.svc.stg.001 |
Object Storage |
Yes/No |
Object Storage Service (e.g S3-compatible) |
Table 5-7: Cloud Infrastructure Platform services.
|
Minimum requirements |
Platform Service Examples |
|---|---|
|
Database as a service |
Cassandra |
|
Queue |
Rabbit MQ |
|
LB and HA Proxy |
NGINX, |
|
Service Mesh |
Istio |
|
Security & Compliance |
Calico |
|
Monitoring |
Prometheus |
|
Logging and Analysis |
ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) |
Table 5-7a: Service examples.
5.2 Cloud Infrastructure Software Profiles features and requirements ¶
This section will detail Cloud Infrastructure Software Profiles and associated configurations for the 2 types of Cloud Infrastructure Profiles: Basic and High Performance.
5.2.1 Virtual Compute ¶
Table 5-8 depicts the features and configurations related to virtual compute for the two (2) Cloud Infrastructure Profiles.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
inf ra.com.cfg.001 |
CPU allocation ratio |
value |
N:1 |
1:1 |
|
inf ra.com.cfg.002 |
NUMA alignment |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
inf ra.com.cfg.003 |
CPU pinning |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
inf ra.com.cfg.004 |
Huge Pages |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
inf ra.com.cfg.005 |
Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
Table 5-8: Virtual Compute features and configuration for the 2 types of Cloud Infrastructure Profiles.
Table 5-9 lists the features related to compute acceleration for the High Performance profile. The table also lists the applicable Profile-Extensions and Extra Specs that may need to be specified.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Profil e-Extensions |
Profile Extra Specs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.001 |
IPSec Acceleration |
Yes/No |
Compute Intensive GPU |
|
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.002 |
Transcoding Acceleration |
Yes/No |
Compute Intensive GPU |
Video Transcoding |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.003 |
Programmable Acceleration |
Yes/No |
Firmware- programmable adapter |
Accelerator |
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.004 |
GPU |
Yes/No |
Compute Intensive GPU |
|
|
infra.com .acc.cfg.005 |
FPGA/other Acceleration H/W |
Yes/No |
Firmware- programmable adapter |
Table 5-9: Virtual Compute Acceleration features.
5.2.2 Virtual Storage ¶
Table 5-10 and Table 5-11 depict the features and configurations related to virtual storage for the two (2) Cloud Infrastructure Profiles.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.stg.cfg.001 |
Catalogue storage Types |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
|
infra.stg.cfg.002 |
Storage Block |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
|
infra.stg.cfg.003 |
Storage with replication |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
infra.stg.cfg.004 |
Storage with encryption |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
Table 5-10: Virtual Storage features and configuration for the two (2) profiles.
Table 5-11 depicts the features related to Virtual storage Acceleration
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.s tg.acc.cfg.001 |
Storage IOPS oriented |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
infra.s tg.acc.cfg.002 |
Storage capacity oriented |
Yes/No |
N |
N |
Table 5-11: Virtual Storage Acceleration features.
5.2.3 Virtual Networking ¶
Table 5-12 and Table 5-13 depict the features and configurations related to virtual networking for the 2 types of Cloud Infrastructure Profiles.
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra. net.cfg.001 |
Connection Point interface |
IO vir tualisation |
virtio1.1 |
virtio1.1* |
|
infra. net.cfg.002 |
Overlay protocol |
Protocols |
VXLAN, MPLSoUDP, GENEVE, other |
VXLAN, MPLSoUDP, GENEVE, other |
|
infra. net.cfg.003 |
NAT |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
|
infra. net.cfg.004 |
Security Group |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
|
infra. net.cfg.005 |
Service Function Chaining |
Yes/No |
N |
Y |
|
infra. net.cfg.006 |
Traffic patterns symmetry |
Yes/No |
Y |
Y |
Table 5-12: Virtual Networking features and configuration for the 2 types of SW profiles.
Note: * might have other interfaces (such as SR-IOV VFs to be directly passed to a VM or a Pod) or NIC-specific drivers on guest machines transiently allowed until mature enough solutions are available with a similar efficiency level (for example regarding CPU and energy consumption).
|
Reference |
Feature |
Type |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.net .acc.cfg.001 |
vSwitch optimisation (DPDK) |
Yes/No and SW Optimisation |
N |
Y |
|
infra.net .acc.cfg.002 |
SmartNIC (for HW Offload) |
Yes/No |
N |
Optional |
|
infra.net .acc.cfg.003 |
Crypto acceleration |
Yes/No |
N |
Optional |
|
infra.net .acc.cfg.004 |
Crypto Acceleration Interface |
Yes/No |
N |
Optional |
Table 5-13: Virtual Networking Acceleration features.
5.3 Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profile description ¶
The support of a variety of different workload types, each with different (sometimes conflicting) compute, storage, and network characteristics, including accelerations and optimizations, drives the need to aggregate these characteristics as a hardware (host) profile and capabilities. A host profile is essentially a “personality” assigned to a compute host (also known as physical server, compute host, host, node, or pServer). The host profiles and related capabilities consist of the intrinsic compute host capabilities (such as number of CPU sockets, number of cores per CPU, RAM, local disks and their capacity, etc.), and capabilities enabled in hardware/BIOS, specialised hardware (such as accelerators), the underlay networking, and storage.
This chapter defines a simplified host, profile and related capabilities model associated with each of the different Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profile and related capabilities; the two profiles (aka host profiles, node profiles, hardware profiles) and some of their associated capabilities are shown in Figure 5-4 .
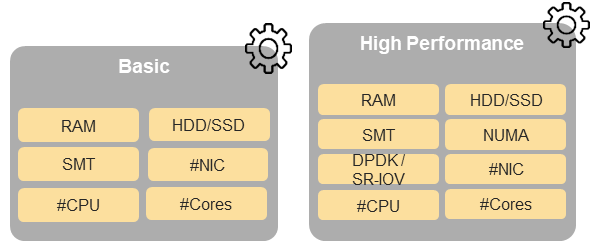
Figure 5-4: Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profiles and host associated capabilities.
The profiles can be considered to be the set of EPA-related (Enhanced Performance Awareness) configurations on Cloud Infrastructure resources.
Note: In this chapter we shall not list all of the EPA-related configuration parameters.
A given host can only be assigned a single host profile; a host profile can be assigned to multiple hosts. In addition to the host profile, profile-extensions and additional capability specifications for the configuration of the host can be specified. Different Cloud Service Providers (CSP) may use different naming standards for their host profiles. For the profiles to be configured, the architecture of the underlying resource needs to be known.
|
Ref |
Cloud In frastructure Resource |
Type |
Defi nition/Notes |
Capabilities Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.hw.001 |
CPU Architecture |
Values such as x64, ARM, etc. |
` e.cap.020` |
The host profile properties are specified in the following sub-sections. The following diagram ( Figure 5-5 ) pictorially represents a high-level abstraction of a physical server (host).
Figure 5-5: Generic model of a compute host for use in Host Profile configurations.
5.4 Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profiles features and requirements. ¶
The configurations specified in here will be used in specifying the actual hardware profile configurations for each of the Cloud Infrastructure Hardware Profiles depicted in Figure 5-4 .
5.4.1 Compute Resources ¶
|
Reference |
Feature |
Description |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.hw .cpu.cfg.001 |
Minimum number of CPU sockets |
Specifies the minimum number of populated CPU sockets within each host* |
2 |
2 |
|
infra.hw .cpu.cfg.002 |
Minimum number of cores per CPU |
Specifies the number of cores needed per CPU* |
20 |
20 |
|
infra.hw .cpu.cfg.003 |
NUMA alignment |
NUMA alignment enabled and BIOS configured to enable NUMA |
N |
Y |
|
infra.hw .cpu.cfg.004 |
Simultaneous Mu ltithreading (SMT) |
SMT enabled that allows each core to work multiple streams of data si multaneously |
Y |
Y |
* Please note that these specifications are for general purpose servers normally located in large data centres. Servers for specialised use with the data centres or other locations, such as at edge sites, are likely to have different specifications.
Table 5-14: Minimum sizing and capability configurations for general purpose servers.
5.4.1.1 Compute Acceleration Hardware Specifications ¶
|
R eference |
Feature |
Des cription |
Basic |
High Per formance |
Capa bilities R eference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infr a.hw.cac .cfg.001 |
GPU |
GPU |
N |
Optional |
|
|
infr a.hw.cac .cfg.002 |
FP GA/other Acce leration H/W |
HW Acce lerators |
N |
Optional |
|
Table 5-15: Compute acceleration configuration specifications.
5.4.2 Storage Configurations ¶
|
Reference |
Feature |
Description |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infr a.hw.stg.hd d.cfg.001* |
Local Storage HDD |
Hard Disk Drive |
||
|
infr a.hw.stg.ss d.cfg.002* |
Local Storage SSD |
Solid State Drive |
Recommended |
Recommended |
Table 5-16: Storage configuration specification.
Note: *This specified local storage configurations including # and capacity of storage drives.
5.4.3 Network Resources ¶
5.4.3.1 NIC configurations ¶
|
Reference |
Feature |
Description |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.h w.nic.cfg.001 |
NIC Ports |
Total number of NIC Ports available in the host |
4 |
4 |
|
infra.h w.nic.cfg.002 |
Port Speed |
Port speed specified in Gbps (minimum values) |
10 |
25 |
Table 5-17: Minimum NIC configuration specification.
5.4.3.2 PCIe Configurations ¶
|
Reference |
Feature |
Description |
Basic |
High Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infra.h w.pci.cfg.001 |
PCIe slots |
Number of PCIe slots available in the host |
8 |
8 |
|
infra.h w.pci.cfg.002 |
PCIe speed |
Gen 3 |
Gen 3 |
|
|
infra.h w.pci.cfg.003 |
PCIe Lanes |
8 |
8 |
Table 5-18: PCIe configuration specification.
5.4.3.3 Network Acceleration Configurations ¶
|
R eference |
Feature |
Des cription |
Basic |
High Per formance |
Capa bilities R eference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
infr a.hw.nac .cfg.001 |
Crypto Acce leration |
IPSec, Crypto |
N |
Optional |
|
|
infr a.hw.nac .cfg.002 |
SmartNIC |
offload network funct ionality |
N |
Optional |
|
|
infr a.hw.nac .cfg.003 |
Com pression |
Optional |
Optional |
||
|
infr a.hw.nac .cfg.004 |
SR-IOV over PCI-PT |
SR-IOV |
N |
Optional |
|
Table 5-19: Network acceleration configuration specification.